GOALS
The heterogeneous prior education of students in introductory computer science courses poses particular challenges for universities, as computer science education varies significantly across German federal states. To address this issue, I developed the practice platform GOALS (Graph Oriented and AI-Based Learning Siegen) together with student assistants, multiple bachelor's and master's theses (under my supervision), Marc Sauer, and Dr. Andreas Hoffmann. GOALS allows students to decide for themselves when to work on which tasks and presents the learning content transparently in a concept graph. By integrating Large Language Models (LLMs), immediate, formative feedback on programming tasks is generated (see Tutor-Kai). Currently, GOALS is used for the introductory computer science lectures Object-Oriented and Functional Programming (OFP) and Algorithms and Data Structures (AuD). The Lecuture Linker project was integrated to provide a context aware chatbot to students. We are also working on integrating the Database Systems lecture (Project ADLER).
Intro Video for Students
Navigation and Progress
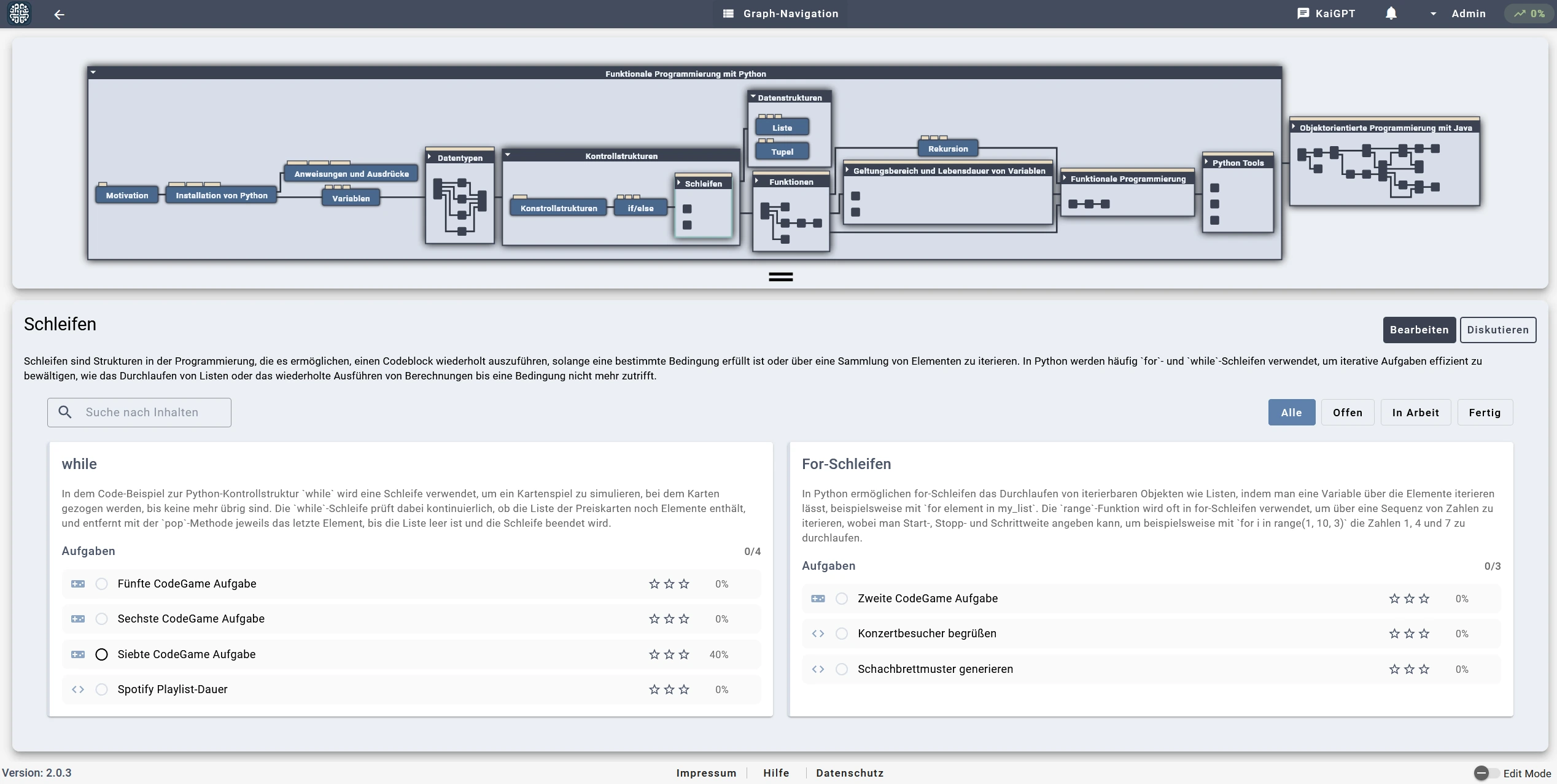
The concept graph enables students to navigate their learning path self-determinedly by transparently visualizing the dependencies between different programming concepts, which are organized into simplified subgraphs to facilitate oversight. Our system maps the targeted competence promotion levels directly to the categories of the cognitive process dimension defined in Anderson and Krathwohl's taxonomy. Within the user interface, these taxonomic categories are simplified and displayed as distinct visual levels assigned to specific tasks, allowing students to easily identify the cognitive demand associated with each exercise.
Different Task Types
Programming Tasks
Students can solve Python, Java, and C++ tasks. For this, we integrated Tutor-Kai (my PhD project).
SQL Tasks
Students can solve SQL (Query and Data Manipulation) tasks. To learn more about this, look at our current Adler project, which also integrates Tutor-Kai tutoring feedback.
Single- and Multiple Choice Tasks
With single and multiple choice tasks, students can demonstrate their understanding and retention of lecture content.
UML Modeling Tasks
Students can practice designing UML class diagrams. Submissions are automatically compared against a reference solution. Additionally, learners receive feedback similar to the feedback types provided by Tutor-Kai. This was developed during a master project group and integrated into GOALS by our student assistant Jan Haas (both under my supervision).

Tasks for Graph- and Tree Algorithms
There are multiple interactive tasks for binary search trees (insert, delete and traversal) and graph algorithms (dijkstra, kruskal, prim, warshal, floyd) with automated assessment and GenAI feedback (see Tutor-Kai). This was developed by our student assistant Taner Kahraman under my supervision. We also created intro videos for students:
CodeGame Tasks
Based on the Kara learning environment students write code (Python, Java, or C++) to navigate a dinosaur character to a target while avoiding obstacles and collecting items. This was developed by Felix Thalmann under my supervision.
- Automated testing features:
- Code restrictions that enforce the use of loops, preventing hardcoded move sequences
- Whitelist and blacklist system for tiles, enabling flexible level design with required and forbidden paths
Video for Students
Editor for Teachers

Related Publications
- Jacobs, S., Sauer, M., & Hoffmann, A. (2025). GOALS: Ein Lern- und Übungssystem für Lehrveranstaltungen im Zeitalter generativer KI am Beispiel einer Einführungsveranstaltung der Informatik. In R. Queckenberg, J. Leschke, & M. Persike (Hrsg.), Learning Analytics, Artificial Intelligence und Data Mining in der Hochschulbildung: Beiträge zur Learning AID 2024 (S. 179–189). transcript Verlag. https://www.transcript-verlag.de/978-3-8376-7583-2/learning-analytics-artificial-intelligence-und-data-mining-in-der-hochschulbildung/
Funding & Resources
This project was funded by the Freiraum 2022 program of Stiftung Innovation in der Hochschullehre.